Dot-com bubble
The largest sectors and companies of the S&P 500 by market capitalization have changed over time. Prior to the dot-com bubble bursting in March 2000 the technology sector made up a third of the S&P 500 thanks to companies such as Microsoft, Cisco, Intel, Lucent Technologies, IBM, America Online and Oracle.
2007-2008 financial crisis
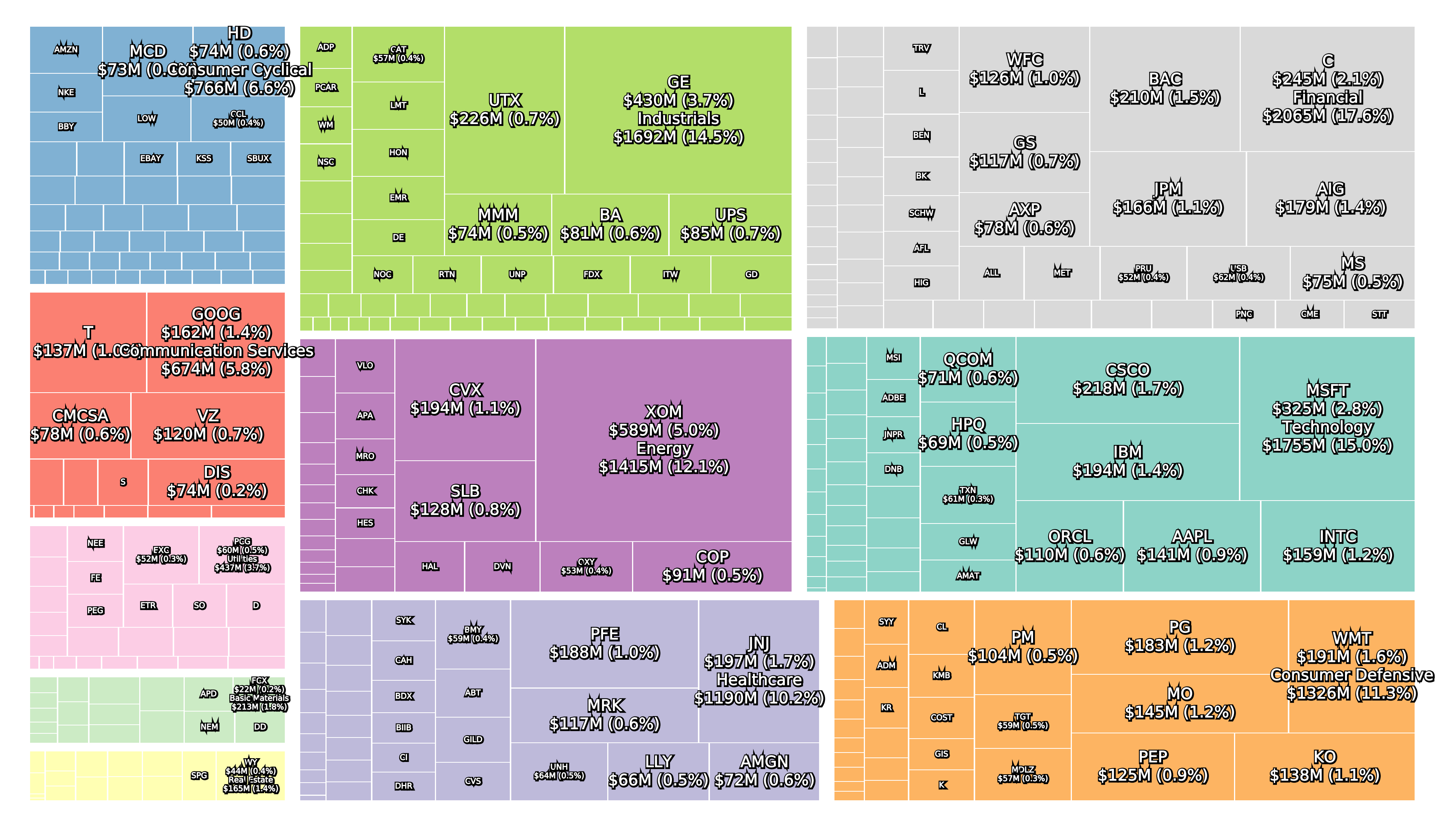
Leading up to the 2007-2008 financial crisis the most valuable sector was the financial sector and some of the most valuable companies were ExxonMobil, General Electric, Citigroup and AIG.
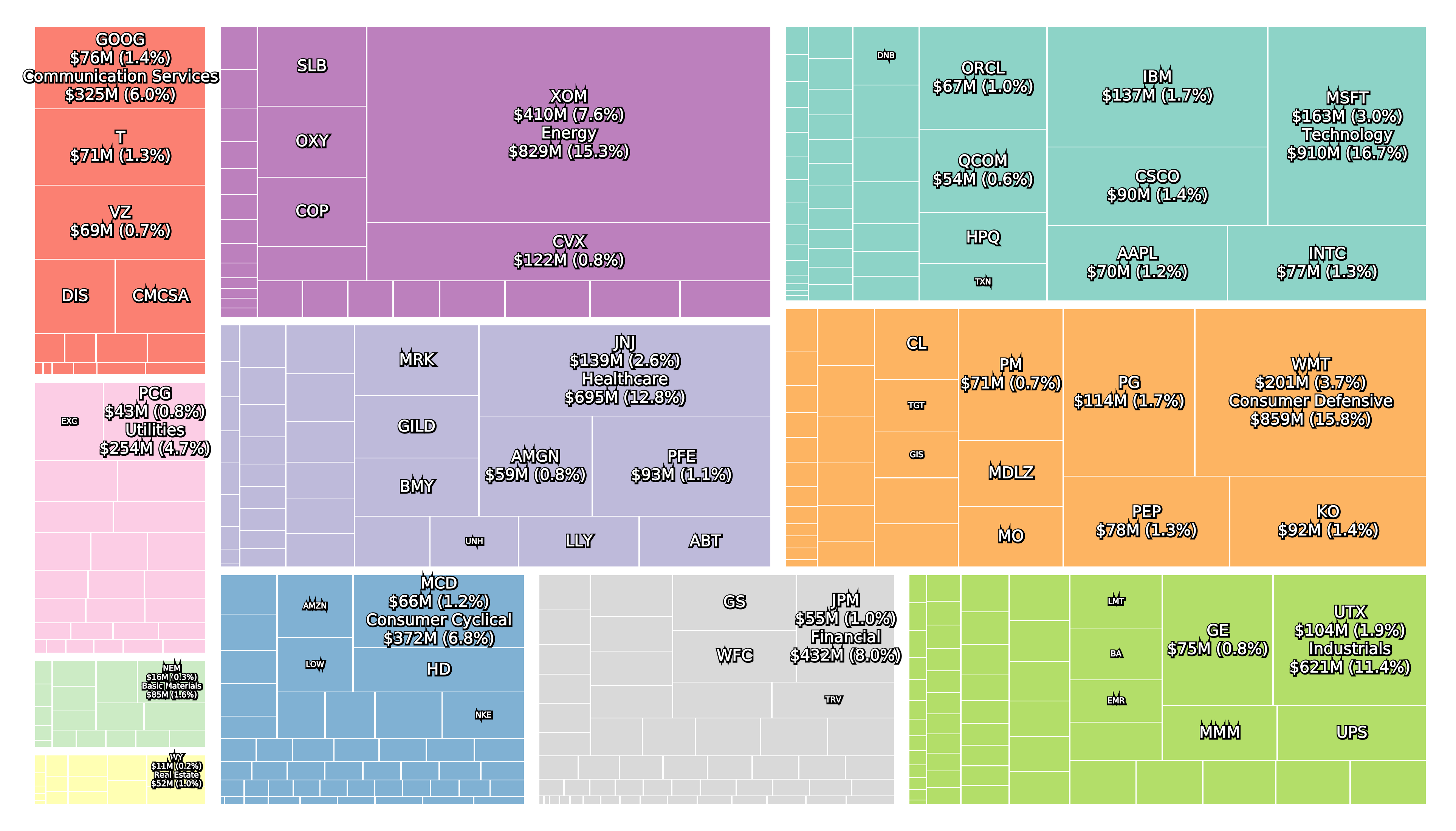
The two figures below show the composition of the S&P 500 at the peak of October 9th 2007 and the bottom on March 9th 2009.
Amazon was added to the S&P 500 on November 18th 2005. and Google was added on April 3rd 2006 after going public in August 2004. However, Berkshire Hathaway was not added until 2010 after a split into A and B shares, and Visa and Facebook did not go public until March 2008 and May 2012, respectively.
The Global Industry Classification Standard (GICS) was changed by MSCI and S&P in 2018. The Telecommunication Services sector was renamed to Communication Services and contains the two industry groups Telecommunication Services and Media & Entertainment. Alphabet and Facebook are two companies in this sector.
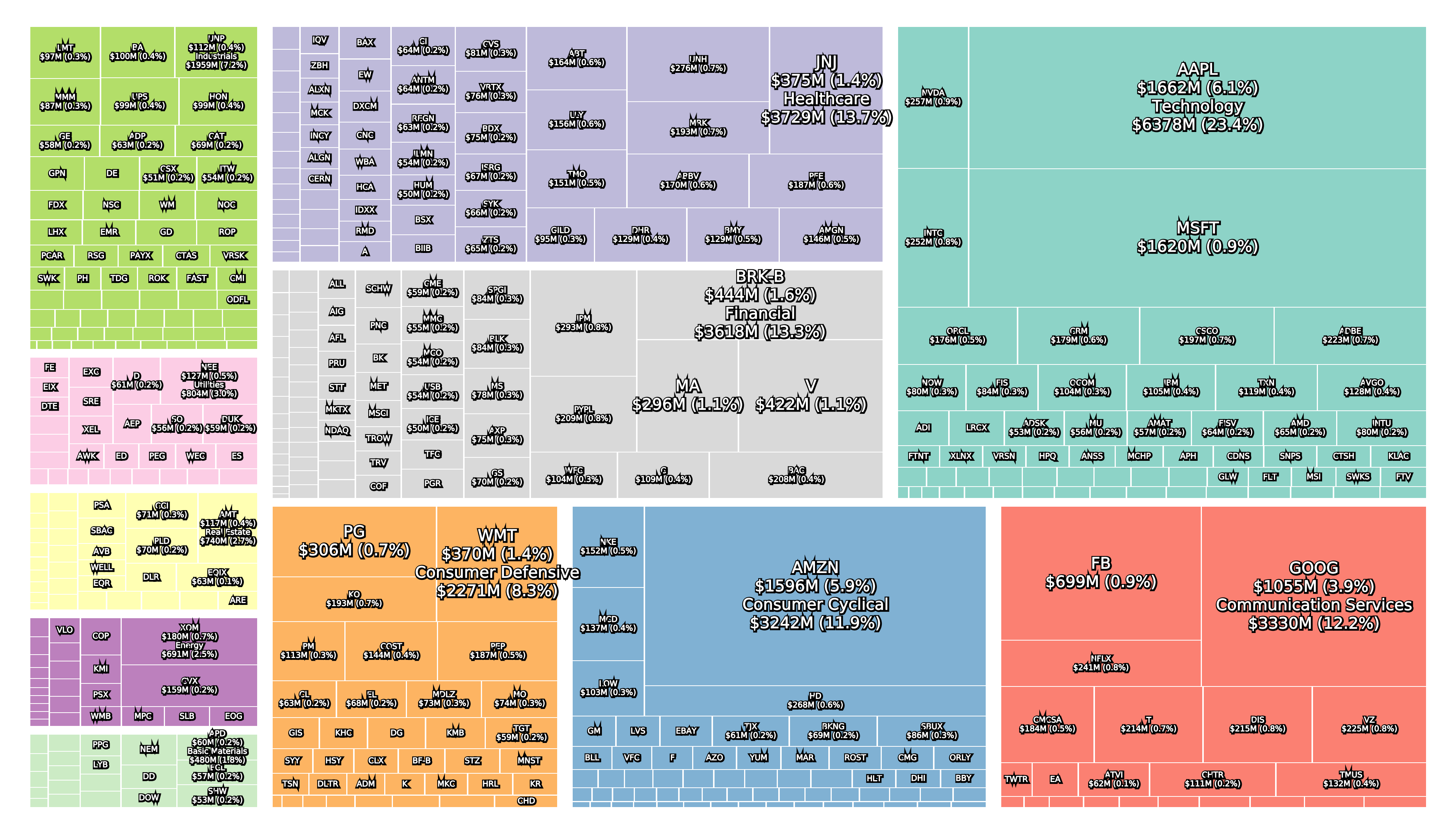
2020 stock market crash
Approximately 200 net additions have been made to the S&P 500 since the 2007-2008 financial crisis.
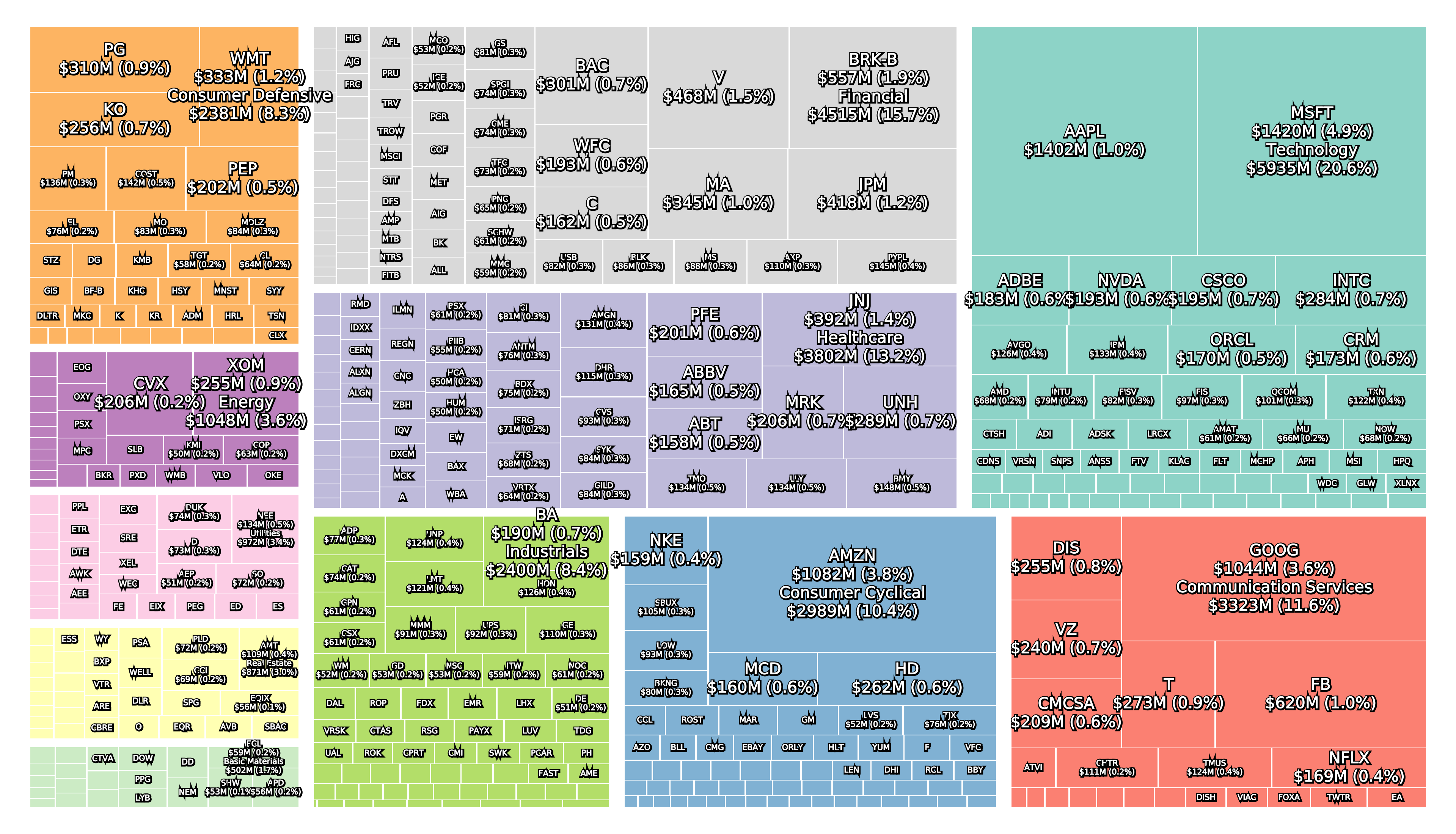
Today (July 2020 following the 2020 crash) the top five (Apple, Microsoft, Amazon, Alphabet and Facebook) make up a quarter of the S&P 500, which is almost unprecedented. The technology sector is the largest and the healthcare sector in 2nd (J&J, UnitedHealth, Amgen, etc.) is larger than the financial sector in 3rd (Berkshire Hathaway, Visa, JP Morgan, etc.). The sectors Communication Services (Alphabet, Facebook, Comcast, Disney, Netflix, etc.) and Consumer Cyclical (Amazon, Home Depot, McDonald’s, etc.) are 4th and 5th. The energy sector is only the 10th largest sector following the 2020 oil price war and ExxonMobil is still the most valuable company in the sector.
The three figures below show the sector composition of the S&P 500 at the February 19th peak, the March 23rd bottom and today (July 10th).
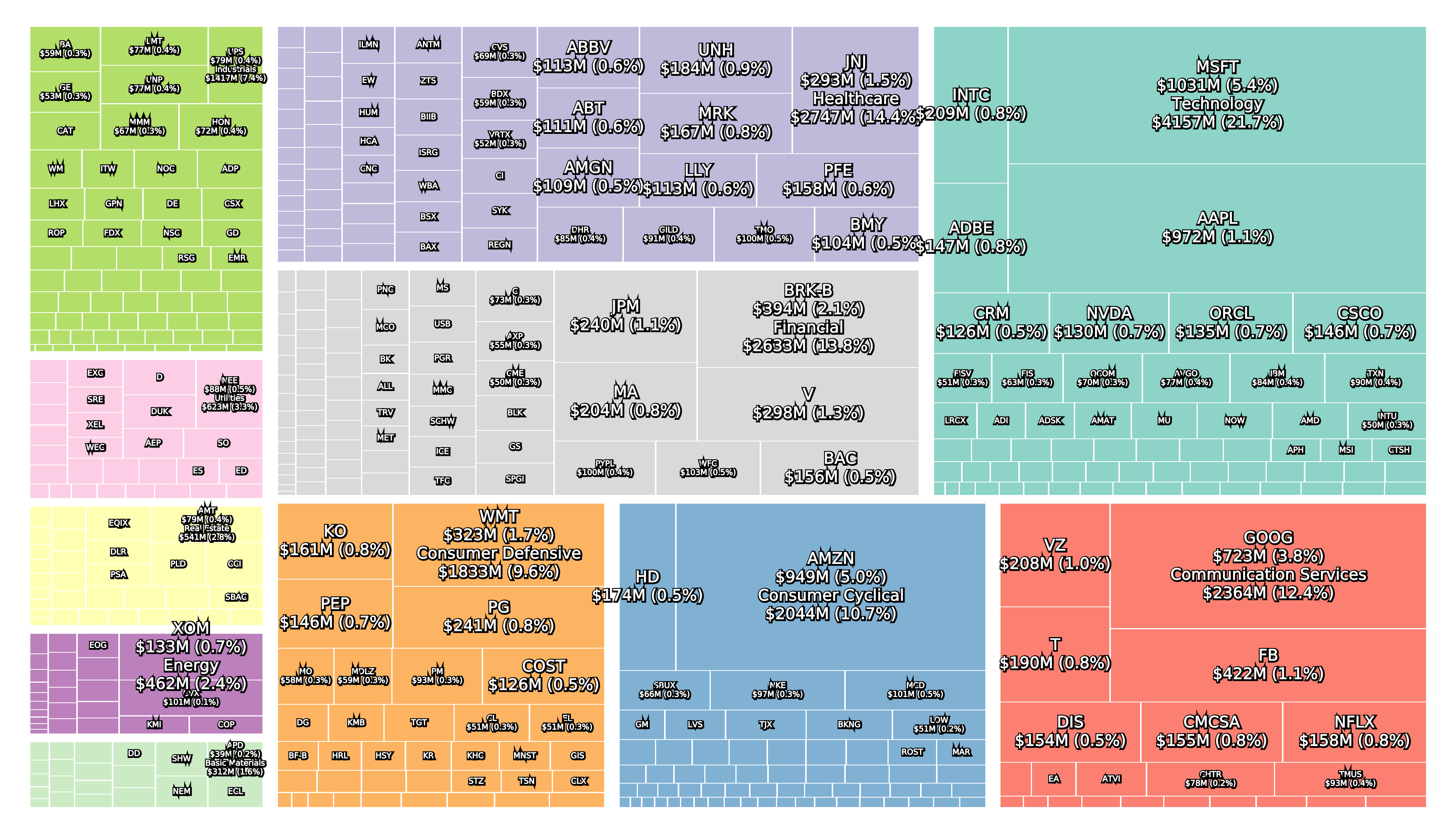

Companies that disappeared
Some companies that were in the S&P 500 before september 2008 have since disappeared not only from the index but entirely. Some merged, some went bankrupt, some were split up and some went private.
Chesapeake Energy ($CHK) filed for bankruptcy in June 2020. Diamond Offshore Drilling ($DO) filed for bankruptcy in April 2020. Frontier Communications ($FTR) filed for bankruptcy in April 2020. J. C. Penney ($JCP) filed for bankruptcy in May 2020.
Allergan ($AGN) was acquired by AbbVie ($ABBV) in May 2020. AbbVie itself was spun off from Abbott in 2013. United Technologies ($UTX) merged with Raytheon ($RTN) in april 2020 after spinning off Otis ($OTIS) and Carrier ($CARR). Spring Corporation ($S) merged with T-Mobile US ($TMUS) in April 2020.
AK Steel Holding ($AKS) was acquired by Cleveland-Cliffs Inc. ($CLF) in 2020. Altera ($ALTR) was acquired by Intel ($INTC). Fortune Brands was split up in 2011 and Beam ($BEAM) was acquired by Suntory in 2014. Compuware ($CPWR) was acquired by BMC Software in 2020. DELL ($DELL) Dell went public in 1988, private in 2013 and public again in 2018. Dow Chemical ($DOW) merged with DuPont (now $DD) in 2017 and was spun off from DowDuPoint ($DWDP) in 2019. Gannett ($GCI) in 2019 merged with New Media Investment Group, parent of GateHouse Media, which itself went bankrupt in 2013, and continued as Gannett. Ingersoll Rand ($IR) merged with Gardner-Denver in 2020 to form Trane Technologies. Jacobs Engineering Group changed its ticker from $JEC to $J in 2019. Life Technologies ($LIFE) was acquired by Thermo Fisher in 2014. Motorola Mobility ($MMI) was acquired by Google ($GOOG) in 2012. News Corp ($NWSA) spun off 21st Century Fox (FOXA) in 2013. BB&T acquired SunTrust ($STI) to form Truist Financial ($TFC). Sunoco ($SUN) was acquired by Energy Transfer Partners ($ETP) in 2012.